画像をダウンロード mirror reflection of light 143662-Lightspeed mirror reflection
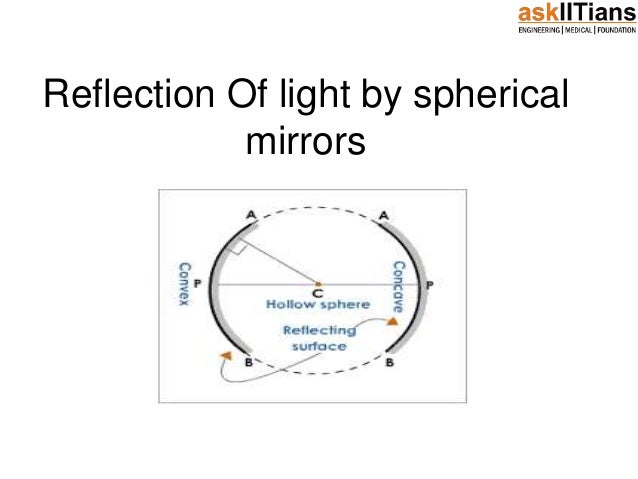
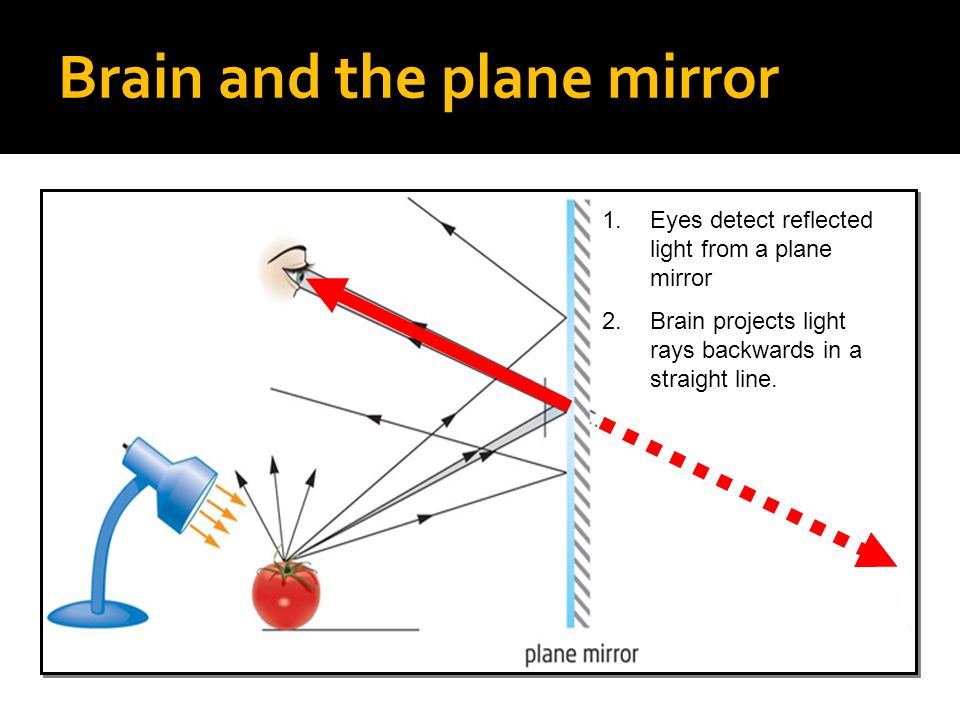
For plane (flat) mirrors, light is reflected according to the law of reflection When the eyes receive these light waves, it looks as if the waves are diverging from behind the mirror, making it appear as if the object is behind the mirror as well This type of image is called a virtual image, because light waves do not actually pass through that point, it only appears soIn a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at a) a flat surface b) a bentin surface c) a bulgingout surface d) an uneven surface Answer The correct option is c) a bulgingout surface Q15 A diverging mirror is a) a plane mirror b) a convex mirror c) a concave mirror d) a shaving mirrorIn a convex mirror the reflection of light takes place at the bulgingout surface or convex surface The back side of a spoon is an example of convex mirror Centre of curvature

Reflection Of Light By Mirror Qs Study
Lightspeed mirror reflection
Lightspeed mirror reflection-In a convex mirror the reflection of light takes place at the bulgingout surface or convex surface The back side of a spoon is an example of convex mirror Centre of curvatureReflection of Light is the process of sending back the light rays which falls on the surface of an object The image formed due to reflection of an object on a plane mirror is at different places



Basic Knowledge Of Reflection Of Light Through Plane Mirror Definition Examples Diagrams
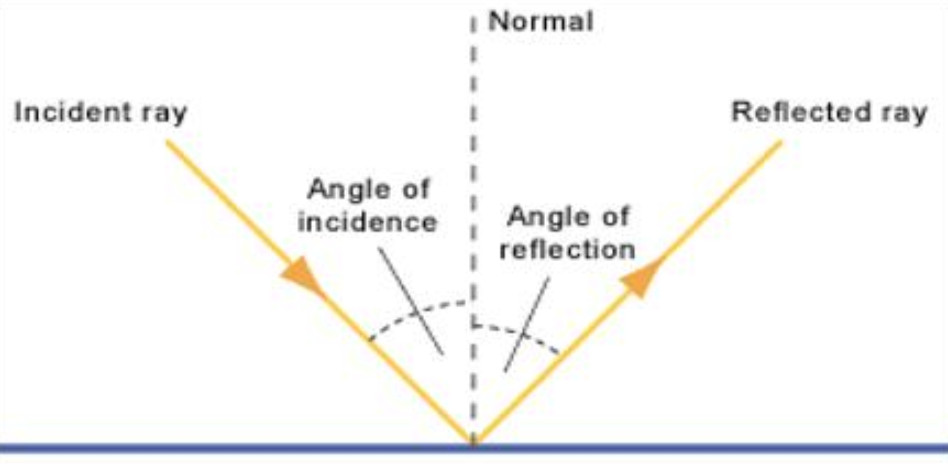
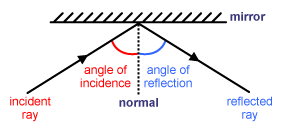
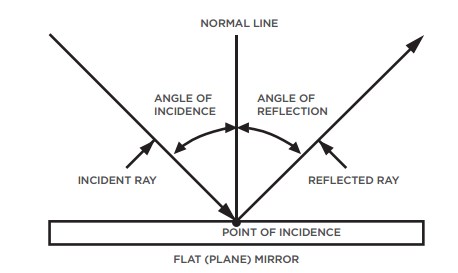
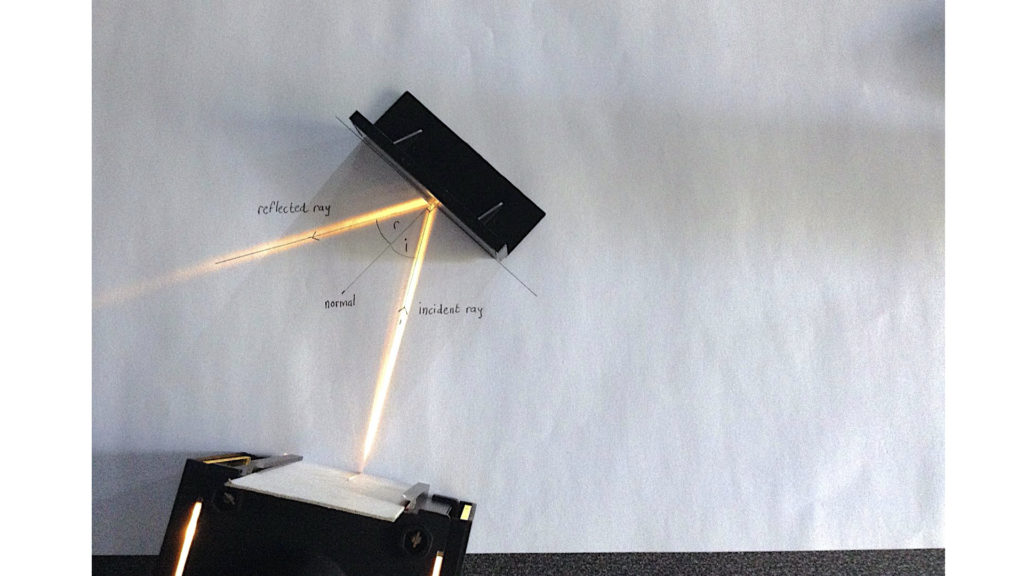
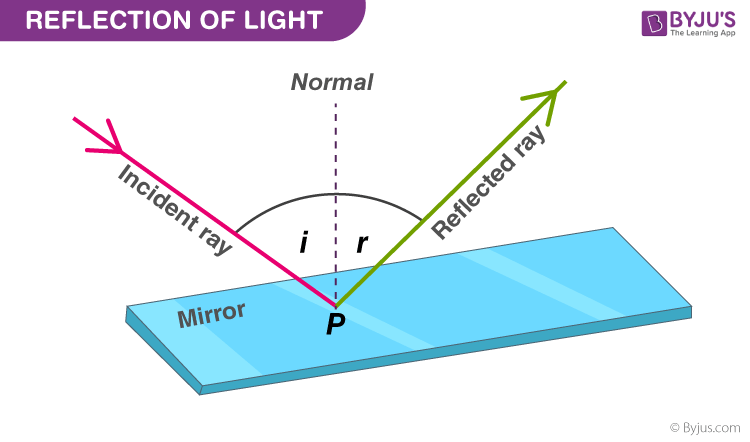
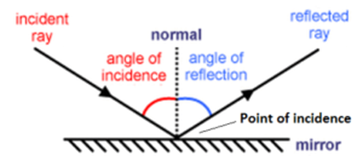
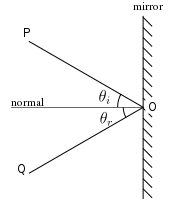
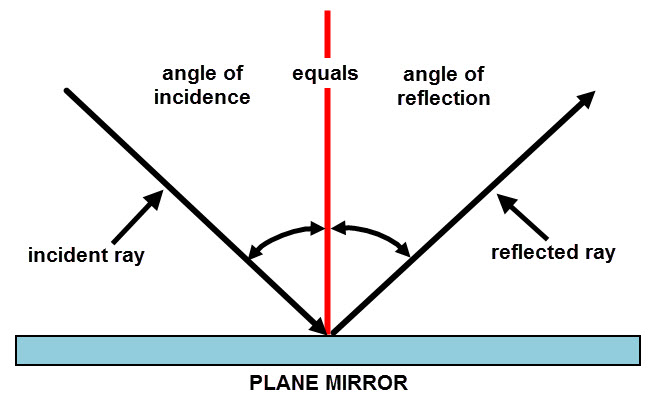
A normal is a line drawn perpendicular to the reflective surface at the point where incident ray hits the surfaceThe angle the light makes with a perpendicular when moving towards the mirror is called the angle of incidence and the angle the light makes moving away from the mirror is called the angle of reflection In optics, we say that when light reflects, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflectionIn a mirror that bulges outward at the center (a diverging mirror or convex mirror), the opposite happens Light rays seem to come from behind the mirror and reflections will appear smaller and further away than they would in a plane mirror Driving mirrors work like this (and so does the back of a spoon if you hold it just right)
Set up a simple mirror activity for preschool and kindergarten science play!In order to understand mirrors, we first must understand lightThe law of reflection says that when a ray of light hits a surface, it bounces in a certain way, like a tennis ball thrown against a wall The incoming angle, called the angle of incidence, is always equal to the angle leaving the surface, or the angle of reflectionWhen light hits a surface at a low angle like on a lake atMirror, Mirror on the Wall Angles of Reflection When you look at an object in a mirror, what you see is the reflection of light from that object Reflection involves two types of light rays the incoming, or incident, ray and the outgoing, or reflected, ray
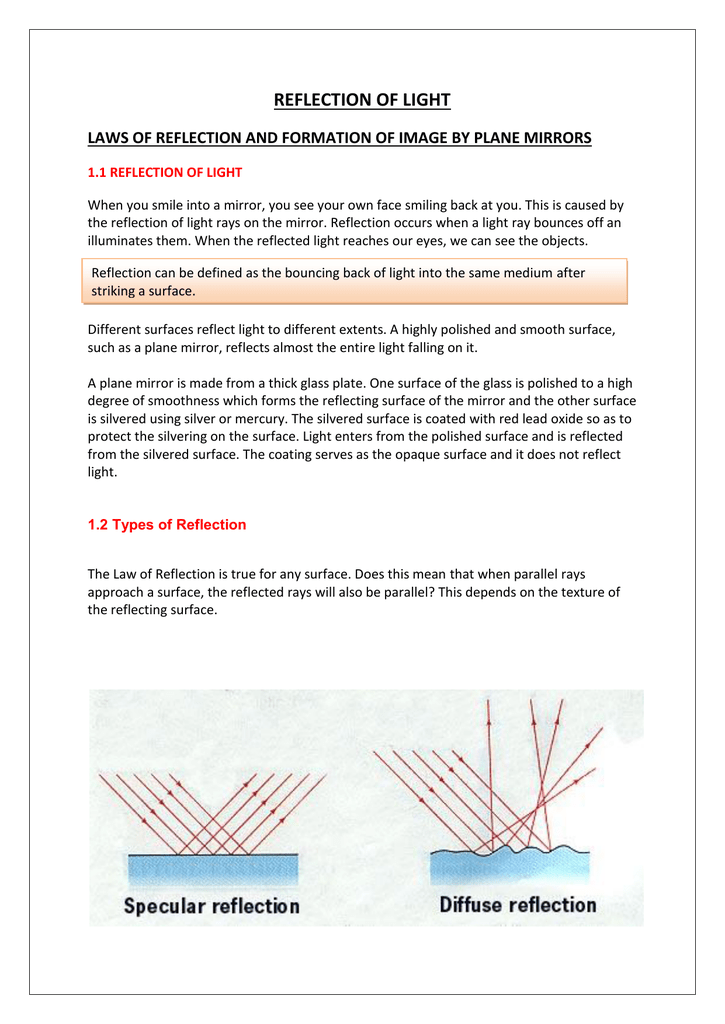
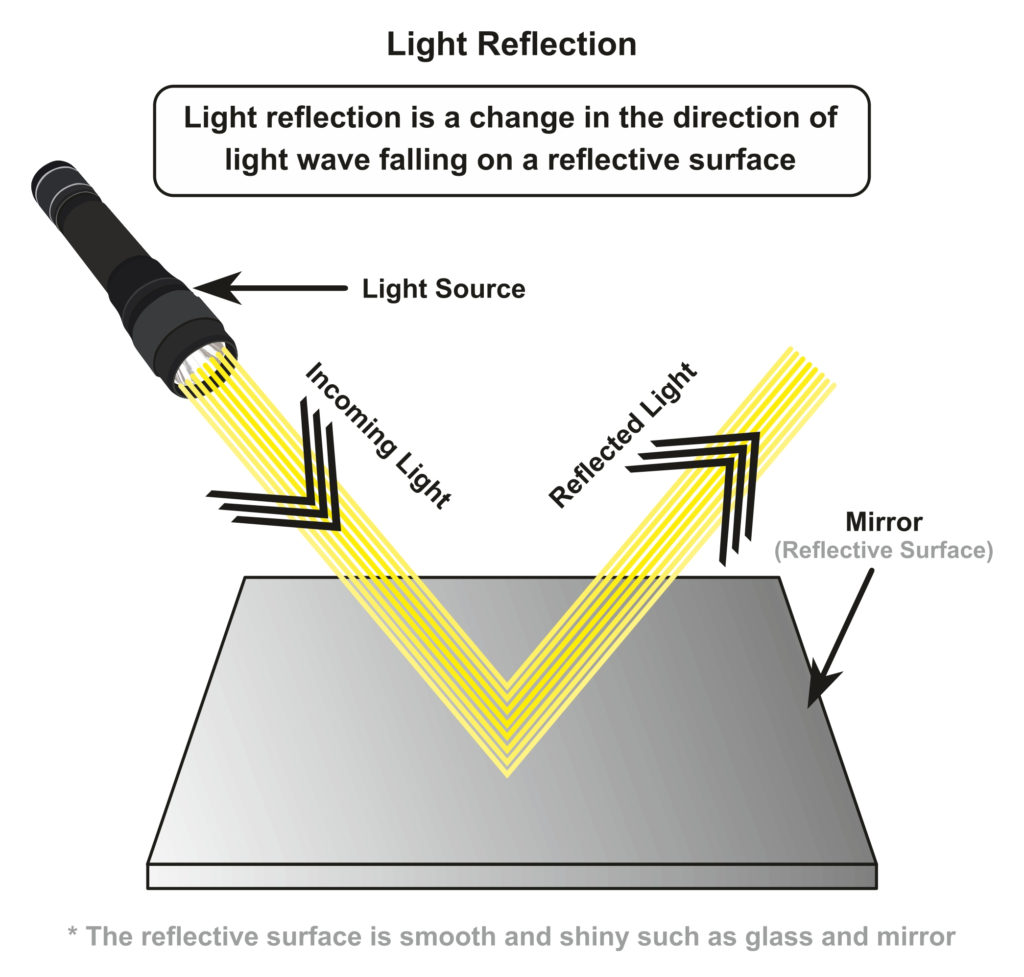
Then this phenomenon is called a reflection of light LAWS OF REFLECTION 1 The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection 2 The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in one plane NOTEa If a ray of light falling normally on a mirror retraces its path on reflection bThe laws of reflection of light are explained here We also discusMirrors reflect light instead of absorbing it, so they trick the eye into thinking the room is brighter and larger, depending on where they are placed Placement



Light And Mirrors Mirror Installation Light Installation Light Art


Reflection Physics Wikipedia
The reflected light produces a mirror image The amount of light reflected by an object, and how it is reflected, is highly dependent upon the degree of smoothness or texture of the surface When surface imperfections are smaller than the wavelength of the incident light (as in the case of a mirror), virtually all of the light is reflected equallyAll materials can be found in your home, at local stores, or on ebay Introduction When we think of reflection, we think of mirrors But reflection can also occur with sound and waves (of water) Specular reflection (such as with mirrors) is used not only to see ourselves, but can also magnify things such as visual images and heatClick Here for Full Physics Course http//bitly/2CZXQuiReflection of Light is Made Easy!


Q Tbn And9gct3slawyjbaaajkmmedwz5svgdep6xszidwe78qq1c Usqp Cau


Reflections Light Shadows And Reflection
Specifically, students will use mirrors and flashlights to investigate how light is reflected from a surface By doing that, they will discover that when a light ray hits a reflective surface, its angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, which is stated by the law of reflectionA virtual image created by the reflection of light from a mirror will always appear to be behind the mirror creating it which is impossible since light does not pass through the image but is reflected This is why it is referred to as a point of apparent divergence Any image you see reflected by a plane flat mirror is a virtual imageUsing the law of reflection, you can predict where a light ray will go after hitting a smooth, reflective surface such as a mirror In fact, you can draw a diagram of the light's path through a mirror maze if the incident angle for the first mirror is known An example of such a diagram is shown in Figure 4



Reflection And Mirrors



Reflection Of Parallel Light Beams From A Concave Mirror Youtube
Reflectionoflightinsphericalmirror#physicsclass8#physivsclass8chapter5inmalayalamhi students, Today we are starting a new chapter REFREFLECTION OF LIGHT IN SAdd a flashlight, spinning tops, a smaller mirror and other objects to create a simple science lesson Kids science experiments and STEM activities can be super simple to do!The Door of Shadows didn't seem to be working for me for whatever reason I couldn't enter the archways (except by backing in), and I couldn't enter the mirror I finally stood very close to the mirror, with my back to it, and disengaged through it Was the only thing that seemed to work Hope this helps somebody


Molecular Expressions Science Optics And You Light And Color Reflection Of Light



Concave Mirror Reflection Page 1 Line 17qq Com
The light ray reflecting away from the mirror is called the reflected ray What is the Normal, Angle of Incidence and Reflection?View Light__mirror_and_lensespptx from MIC 303 at BRAC University Instructions Topics are going to cover • Electromagnetic waves, • Laws of Reflection and Refraction of Light, • TotalDid you mean reflection light mirror Conair Reflections LED Lighted Collection DoubleSided Makeup Mirror, 1x/7x magnification, Polished Chrome 41 out of 5 stars 1,734 $3999 $ 39 99 Get it as soon as Fri, Dec 18 FREE Shipping by Amazon Arrives before Christmas



Light School Help By Gunjan Light Reflection Light Parts Of Human Eye


Reflection Of Light
Reflection of Light on a Plane Mirror When you look at the image of an object in a plane mirror, the rays of light originating from the object hit the mirror The ray of light that strikes the mirror is known as the incident ray The ray of light which reflects from the mirror The normal is aThe light ray reflecting away from the mirror is called the reflected ray What is the Normal, Angle of Incidence and Reflection?A reflection appears to be the same distance from the "other side" of the mirror as the viewer's eyes are from the mirror Also, when light is reflected from a mirror, it bounces off at the same


Laws Of Reflection


Mirrors Science World
A mirror is a light recycler, which is what makes this experiment so tricky When you add mirrors to a home or a garden, they reflect and recycle the light that enters that space If you add many mirrors, they can bounce the light off each other, and with each bounce, a little bit of light is lostReflection of light The rebound of rays of light from an elegant and glossy surface is called reflection or reflection of light It is related to a football bouncing back after colliding with a wall or any hard surface Laws of Reflection of Light The angle of reflection and incidence are equal The incident ray reflected ray and normal to the point of reflection lies in the same planeReflection of light Waves – including light – can be reflected at the boundary between two different materials The angles of incidence and reflection are measured between the light ray and the



Free Notes For Competition Exam Ssc Ibps Bank Physics For Ssc Cgl Part 3a Light Reflection Plane Mirror Concave And Convex Lens



Physics Form 4 5 1 Understanding Reflection Of Light
Explore light and reflections through hands on play!The light beam is reflected in a particular direction and can only be seen in that direction This is called specular reflection but with children we just call it mirror reflection (Figure 2a and 3a) Mirrors have a very smooth surface In figure 3a we caught this reflection on a piece of paperReflection of light enables us to see the objects around us or we can say that everything we see in this world is because of the reflection of light Objects do not possess their own light, the object is only visible due to reflection of light Source of light can be a Sun or any lightemitting blub etc which produces light energy


Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Light And Color Reflection Of Light



Why Reflected Light From A Mirror Don T Get Absorbed In Polarized Sunglasses Physics Stack Exchange
Experiment Reflection of Light by Mirror Task Reflection of light by mirror Required accessories A plane mirror and a torchlight Procedure Keep the minor on the floor of the room in such a way that its face or the smooth surface remains upward Throw light from the torch in a straight way on the mirror This light will be reflected back from the mirror and fall straight to the roofA normal is a line drawn perpendicular to the reflective surface at the point where incident ray hits the surfaceThe reflection of visible light is a property of the behavior of light that is fundamental in the function of all modern microscopes Light is often reflected by one or more plane (or flat) mirrors within the microscope to direct the light path through lenses that form the virtual images we see in the oculars (eyepieces)


Law Of Reflection



Two Plane Mirrors Make The Angle Alpha 33 0 Circ Between Them A Ray Of Light Incident On One Of The Mirror Is Reflected And Hits The Second Mirror Find The Angle Between
Observe that in this case the light rays diverge after reflecting off the mirror When light rays diverge after reflection, a virtual image is formed As was done with plane mirrors, the image location can be found by tracing all reflected rays backwards until they intersect For every observer, the reflected rays would seem to be diverging from this pointReflection involves two types of light rays the incoming, or incident, ray and the outgoing, or reflected, ray The angle between the incident ray and an imaginary perpendicular line drawn to the surface of the mirror is called the angle of incidenceREFLECTION OF LIGHT BY SPHERICAL MIRROR REFLECTION OF LIGHT When light strikes the surface of an object, some of the light is returned into the same medium OBJECT AND IMAGE The concept of an object is before the phenomena of reflection and refraction of light and the concept PROPERTIES OF



Optical Experiment Demonstration Of Reflection Of A Light Beam In A Mirror Stock Image Image Of Abstract Glass



How To Reflect A Beam Of Light On A Mirror Using Cycles Blender Stack Exchange
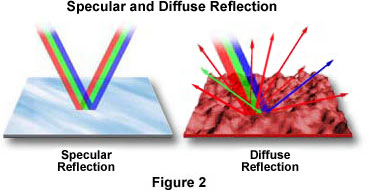
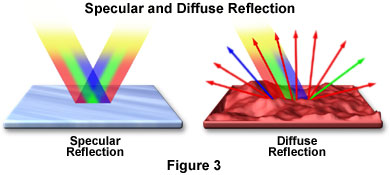
The Reflection of Light In specular reflection, the reflected rays are parallel to each other In diffuse reflection, light is reflected in random directions Flat, reflective surfaces, eg mirrors, polished metal, surface of a calm pond of water Rough surfaces, eg paper, wood, unpolished metal, surface of a pond on a windy dayMirror, Mirror on the Wall Angles of Reflection When you look at an object in a mirror, what you see is the reflection of light from that object Reflection involves two types of light rays the incoming, or incident, ray and the outgoing, or reflected, rayRays of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection from a convex mirror get diverged and appear to come from a point behind the mirror 6 Terms used in the study of spherical mirrors i) Center of curvature It is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part (C)



Plane Mirror Reflection Youtube



Reflection Of Light In A Mirror Lateral Inversion Physics
Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors Purpose a To study the reflection of light b To study the formation and characteristics of images formed by different types of mirrors Theory When a light (wave) travelling in one medium encounters a boundary of another medium, part of the light bounces back to the same medium, called the ReflectionSuppose a light bulb is placed in front of a concave mirror at a location somewhere behind the center of curvature (C) The light bulb will emit light in a variety of directions, some of which will strike the mirror Each individual ray of light that strikes the mirror will reflect according to the law of reflection Upon reflecting, the light will converge at a pointLaws of Light 1 The angle of incidence = angle of reflection 2 The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal (line perpendicular to the plane of the mirror/ reflective surface) all lie in the same plane



Class 8 Science Light Reflection In Plane Mirrors Youtube



The Law Of Reflection Physics
This is a nonmirrorlike reflection of light In this type of reflection rays of light hit an irregular object with a rough surface, and reflects back in all directions Here, the incident ray which is reflected along with reflected ray doesn't have the same angle to the normal as the incident ray Regular Reflection It is a mirrorlikeWhen light from an object is reflected by a surface, it changes direction It bounces off the surface at the same angle as it hits it Smooth, shiny surfaces such as mirrors and polished metalsThe light beam is reflected in a particular direction and can only be seen in that direction This is called specular reflection but with children we just call it mirror reflection (Figure 2a and 3a) Mirrors have a very smooth surface In figure 3a we caught this reflection on a piece of paper
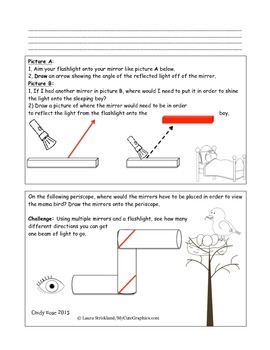


Mirror Mirror A Hands On Light Reflection Activity By Rose Stem
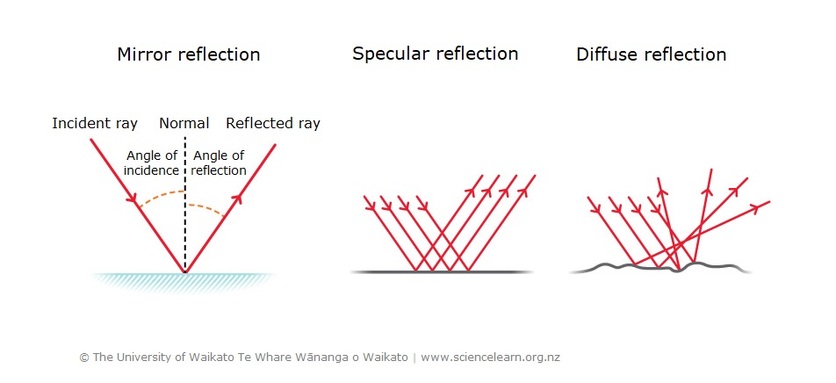


Reflection Of Light Science Learning Hub
Simple Mirror Activity for Kids Exploring Mirrors, Light & Reflection Try a simple mirrorRegular Reflection can also be referred to as Specular Reflection and is simply understood by using a plane mirror This mirror used for reflection of light is not the regular mirror we see around us, rather it is a glass which is heavily coated with a uniform layer of highly reflective material such as a powderIn Investigating reflection students investigate specular and diffuse reflection by looking into a dark box and shining a torch at various objects, coloured paper and a mirror To model blue sky and a red sunset, try shining white light from a torch or a projector into a glass container of water with a few drops of milk in it



Reflection Of Light Laws Types With Videos And Examples


Q Tbn And9gctv6j Kc8jzgh5v Zz8s2d26k4beperjlfiew6ybhjbl6orel4e Usqp Cau
A mirror is an object that reflects an imageLight that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon itReflection of light The throwing back by a body or surface of light without absorbing it, is known as reflection of light A highly polished surface, such as a mirror or other smooth and plane surface, reflects most of the light falling on it Reflection of light is either specular (just like mirror) or diffuse (retaining the energy
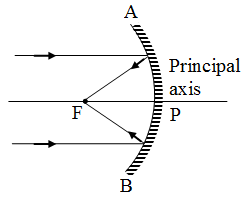


Reflection Of Light From Spherical Mirror A Plus Topper
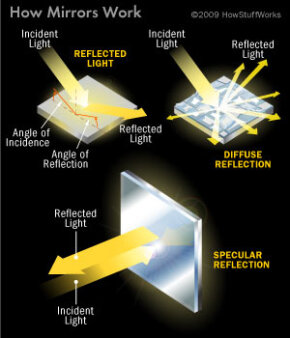


Mirror Physics Howstuffworks



Learn About Applications Of Reflection Of Light Chegg Com



Reflection Of Light By Spherical Mirrors Spherical Mirror Videos Types



The Law Of Reflection Physics


Reflection Mirrors



Reflection Of Light In A Plane Mirror Varying Incidence Angle Youtube



Reflection Of Light By Mirror Qs Study



Mirror Reflections Primaryleap Co Uk Mirror Reflection Science Reflection


The Law Of Reflection Physics


The Open Door Web Site Ib Physics Optics Reflection Of Light
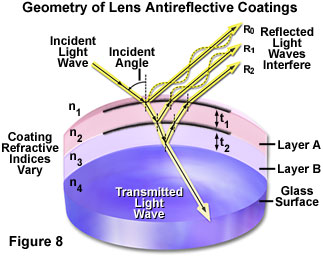


Reflection Of Light Introduction Olympus Ls



The Law Of Reflection


Types Of Reflection Of Light With Laws And Examples


Light Website Reflection



Reflection Of Light By Plane Mirror Videos Concepts And Examples


Reflection Of Light By Spherical Mirrors Physics



It S Presence Is What I Need A Good Friend Indeed Aninagmafae05


The Reflection And Refraction Of Light


Reflections In A Plane Mirror Ppt Download



What Makes Light Reflect Off Of Mirrors



Cheat Sheet 1 Cds Optics Light Plane Mirror Reflection Image Dreams Iq


Mirror Light Reflection Glowforge Edu


Science Fair Projects Light Maze Science Experiments For Kids



Reflection And Light Flat Mirrors Ppt Video Online Download



Snc2p


The Reflection And Refraction Of Light
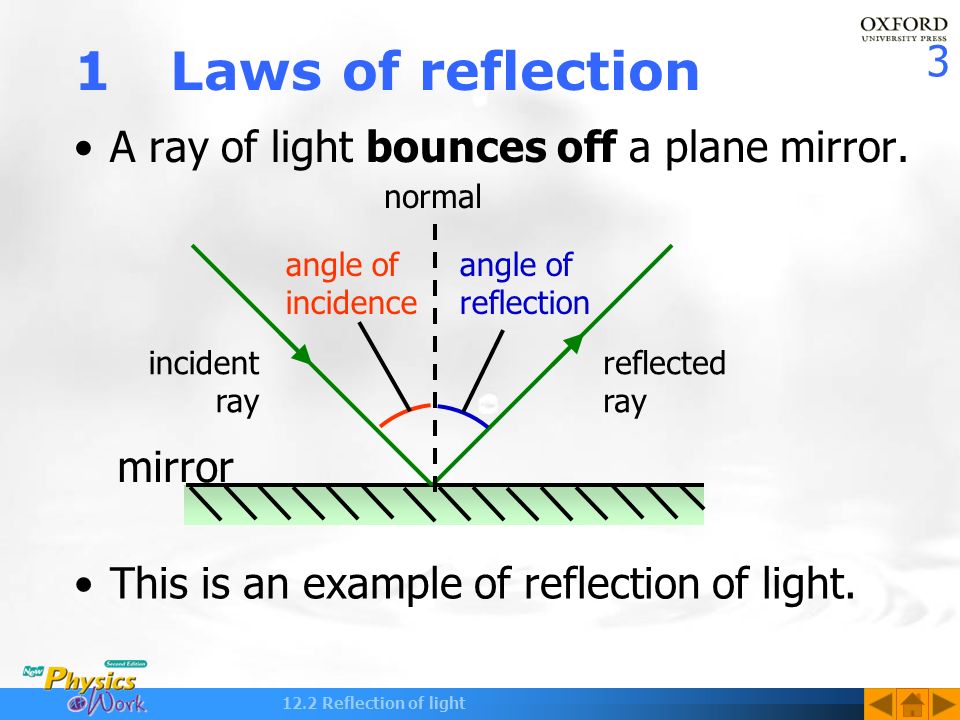


12 2 Reflection Of Light How Do You Look In Others Eyes Ppt Video Online Download


Do Shadows Have Reflections If A Light From A Window Is Shown On A Mirror And Bounces Back To The Wall In Front Of It That You See The Light On The



Model How Light Reflects Off A Mirror With Python Wired


The Law Of Reflection Physics



Physics Optics Light Reflecting 2 Of 4 Plane Mirror Ex 2 Youtube



Ciensacao Hands On Experiment Mirror Targeting Physics Optics Light Mirror Reflection Open Educational Resource
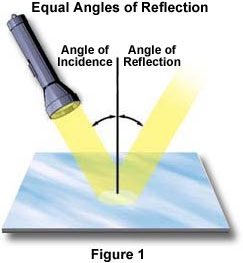


Molecular Expressions Science Optics And You Light And Color Reflection Of Light


Q Tbn And9gct6oyxwsstgyshbjly96xsm4wawcx3a8ues Ooeluk Usqp Cau


Physics Tutorial Reflection Of Light And Image Formation


The Reflection And Refraction Of Light



How Mirrors Work Explain That Stuff



Plane Mirror Reflecting Light Stock Image C026 7657 Science Photo Library
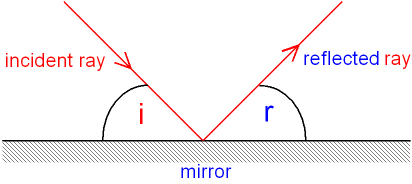


Gcse Physics What Is Reflection Reflection Of Light From A Plane Mirror Angle Of Incidence And Angle Of Reflection Gcse Science



Basic Knowledge Of Reflection Of Light Through Plane Mirror Definition Examples Diagrams



Pin By Lisa Yu On Art Dump Light Art Mirror Art Installation Art



The Hockey Schtick Why Conventional Greenhouse Theory Violates The 1st Law Of Thermodynamics


Mirrors And Reflection Learn Physics Class 6 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network
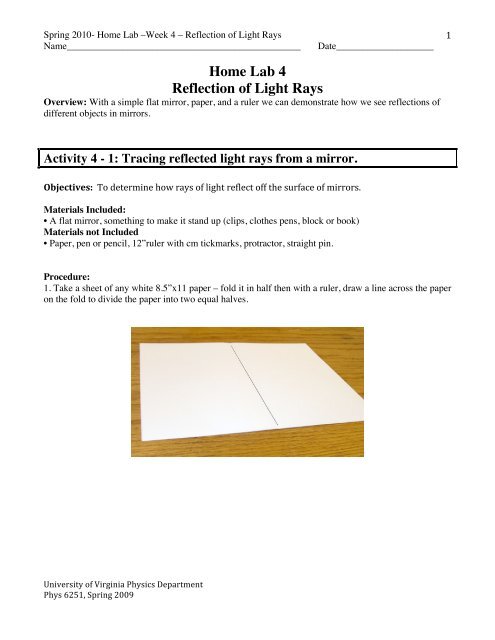


Home Lab 4 Reflection Of Light Rays University Of Virginia


Reflection Refraction And Diffraction



The Reflection Of Light Optics For Kids


What Is Reflection Of Light Definition Laws Types Video



Light Notes Videos Qa And Tests Grade 7 Science Light Kullabs



Light Reflection And Refraction Britannica


Reflection Of Light Meaning Types Characteristics Formation Of Image



How To Draw Ray Diagrams Reflection Of Light Physics Science Letstute Youtube


Reflection Physics Wikipedia



Kids Science Light Reflection Kids Bouncing Light Experiments



Readings Light Reflection Of Light


Why Is Light Reflected Quora


1


The Physics Of Light Curved Mirrors



Light Reflection And Refraction


When A Light Ray Hits A Tilted Mirror Mirror Is At An Angle How Will It Reflect Off The Mirror Quora


Mirrors And Reflection Worksheet Edplace


Reflection In Plane Mirrors Learn Physics Class 8 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network
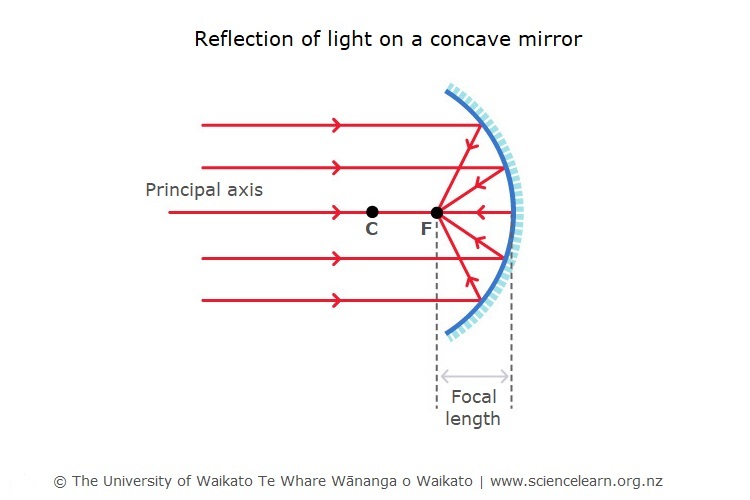


Reflection Of Light Science Learning Hub


Physics Tutorial Reflection Of Light And Image Formation


Physics Tutorial The Law Of Reflection


Untitled Document
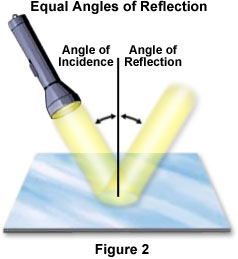


Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Light And Color Reflection Of Light


Experiment 8



Image Formation In A Plane Mirror Youtube
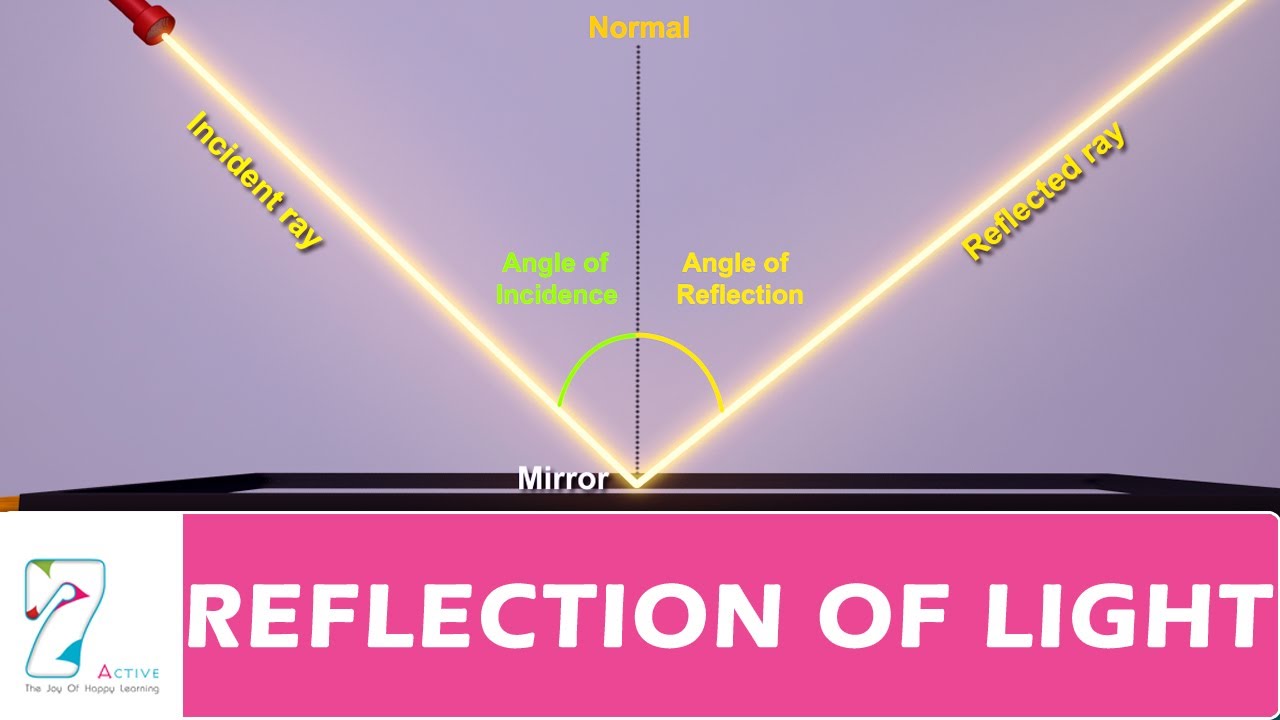


Reflection Of Light Youtube



Roziqorx C By Clairegrenade Via Flickr Light Reflection Light Light Art
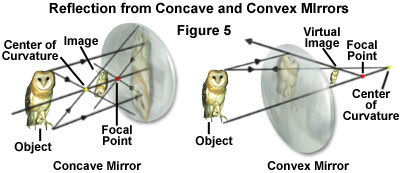


Reflection Of Light Introduction Olympus Ls



Both A Mirror And A 90 Degree Prism Are Not Reflecting Light On To A Screen Cycles Blender Stack Exchange


Mirrors And Reflection Learn Physics Class 6 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network
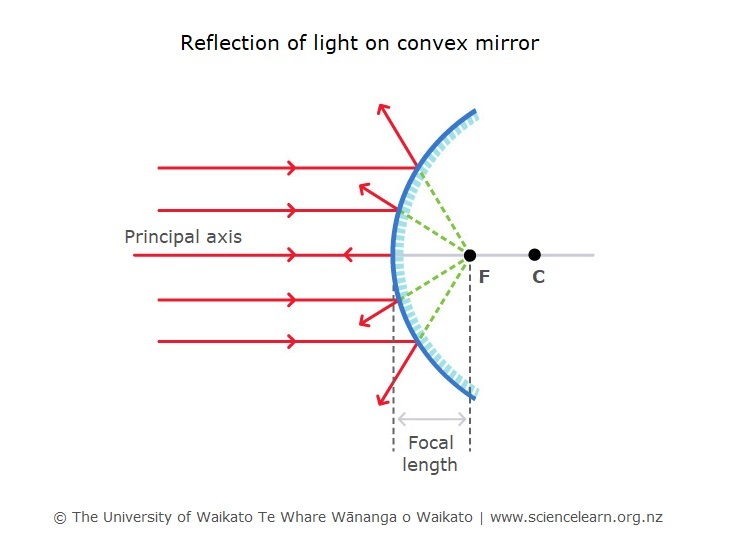


Reflection Of Light Science Learning Hub



Mirrors And Reflection Of Light Science Project Education Com


コメント
コメントを投稿